Don’t invest unless you’re prepared to lose all the money you invest. This is a high-risk investment and you should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong. Take two minutes to learn more.
This article is not intended to be financial, investment or trading advice. This article is for information and solely for education purposes. It does not protect against any financial loss, risk or fraud.
What is The Merge?
The Merge refers to the transition of Ethereum (ETH), which is the second largest cryptocurrency by market cap, from a proof of work (PoW) to a proof of stake (PoS) consensus. As a result, there will be a technical and economic change in how the protocol works, while how ETH is governed will stay the same.
The upgrade has been in the works for years, arguably dating back from Ethereum’s genesis block mined on July 30, 2015. Given the delays in launching the transition, many are in disbelief that the merge is finally about to happen.
The time of The Merge is to be confirmed, but Ethereum developers expect it to happen any day now.
Why is it called 'The Merge'?
In December 2020, a new chain was started named the ‘Beacon chain’. The Beacon chain will become the main PoS chain for Ethereum 2.0 once the current PoW consensus chain merges with it.
This upgrade is complex, hence the creation of the new chain. Associated testing has stretched over almost two years ahead of the final mainnet upgrade.
The diagram below shows the timeline and upgrades that have happened on both chains ready for The Merge.
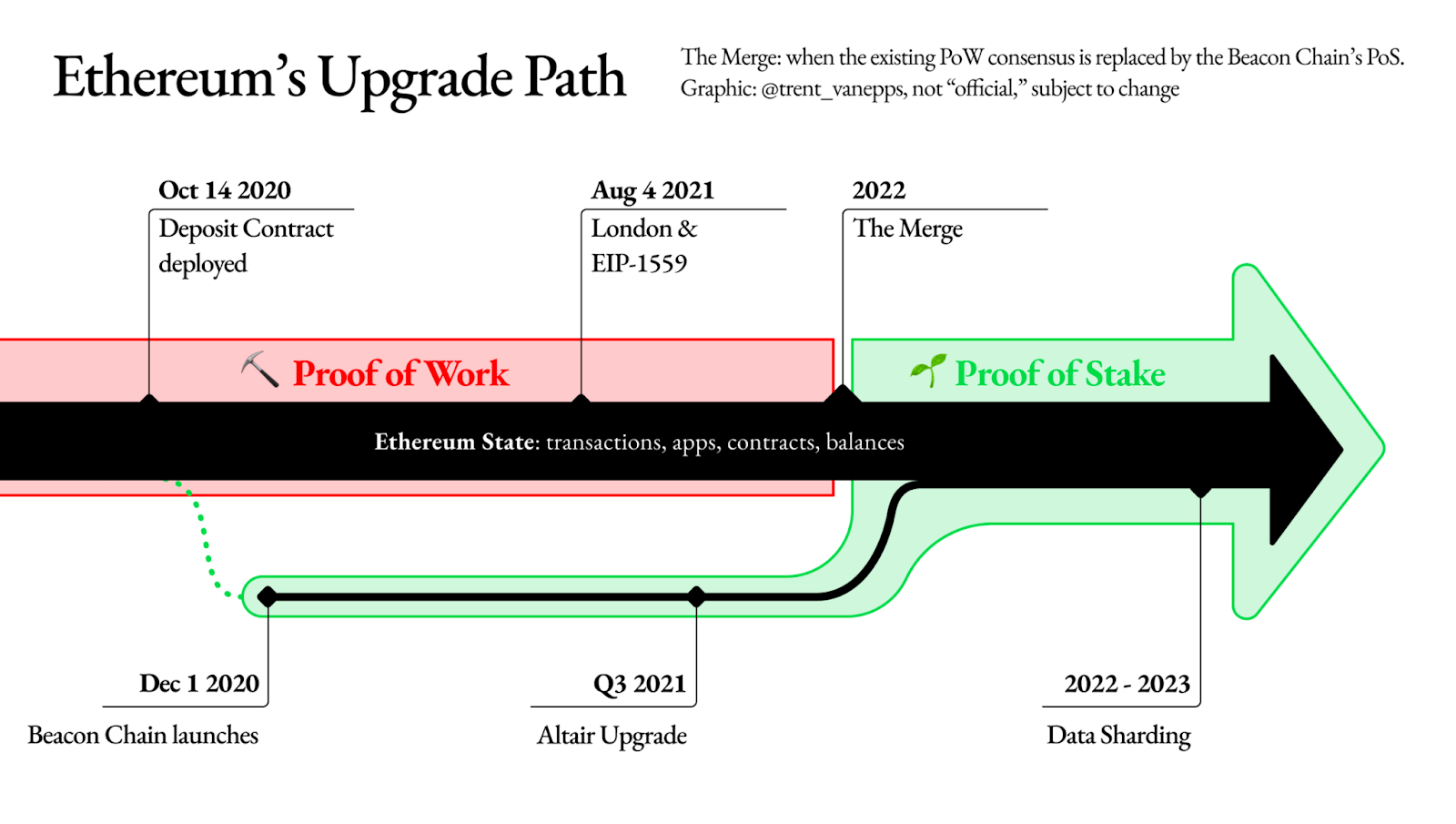
Source: Ethereum Foundation
Why Proof-of-Stake?
Firstly, let’s clarify the differences between PoW and PoS.
In a PoW system, miners spend vast amounts of computing power verifying and adding new blocks to the chain.
In a PoS system, validators stake capital in the form of cryptocurrency to participate in block production. Hence ETH are estimating a ~99.9% reduction in energy consumption because of the merge.
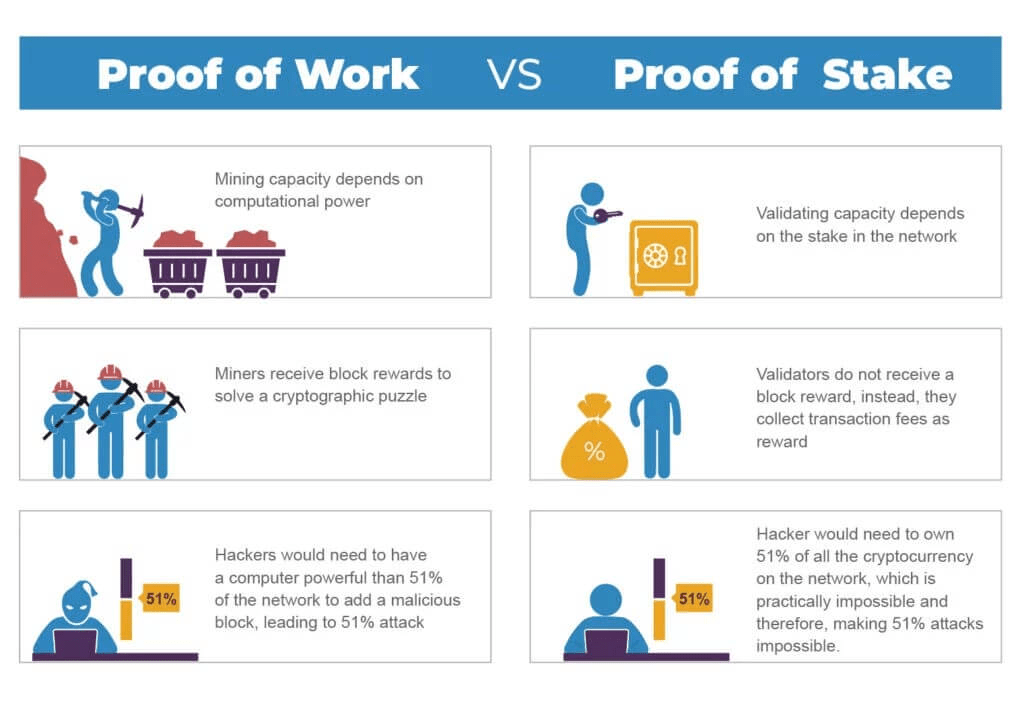
Source: Bitcoinik
What are the advantages of Proof-of-Stake?
1. Increased security
To carry out a 51% attack on the ETH PoW blockchain, it would cost an estimated $800-900K per hour. To attack the ETH 2.0 network, the attack would need to control over 51% of staked ETH and would cost around $10 billion.
On top of that, there are more than 417K active validators already, making the network incredibly resilient.
2. Economic sustainability
Stakers in Ethereum 2.0 currently collect validation fees, but soon they’ll collect a cut of the transaction fees that people pay to use the network. Aside from this, there’s no subsidy paid to miners, meaning there will be significantly less new ETH being issued.
The result: less downward pressure on price and an increased security budget. ETH may well become deflationary after The Merge if usage of the network picks up like it did in 2021.
According to the Coinbase and Ethereum foundation, yields could increase from 4.3% – 5.4% APR to upwards of 9 –12% after The Merge. This would mean hefty profits for validators.
3. Native yield
ETH becoming a yield-bearing asset could be a huge step for the crypto space as it provides a hurdle-rate for the entire industry. Similarly, it could attract significantly more investment from a world where yields are hard to come by.
4. Democratized participation
In a PoW world, economies of scale dictate that only large mining enterprises can participate in block production. In the ETH PoS world, anyone can become a validator if they stake a minimum of 32 ETH, or delegate to a larger entity and indirectly participate and receive rewards.
5. Environmental sustainability
Staking is far less damaging to the environment than PoW mining. In fact, ETH’s environmental footprint will shrink by ~99.95% after the switch to PoS.
6. Increased decentralization
Enabling more people to participate in block production helps make Ethereum more resilient and decentralized. ETH mining is already less centralized than Bitcoin’s, but Ethereum 2.0 will be even more so.
The below charts compare the current mining landscape and the validators on the beacon chain.
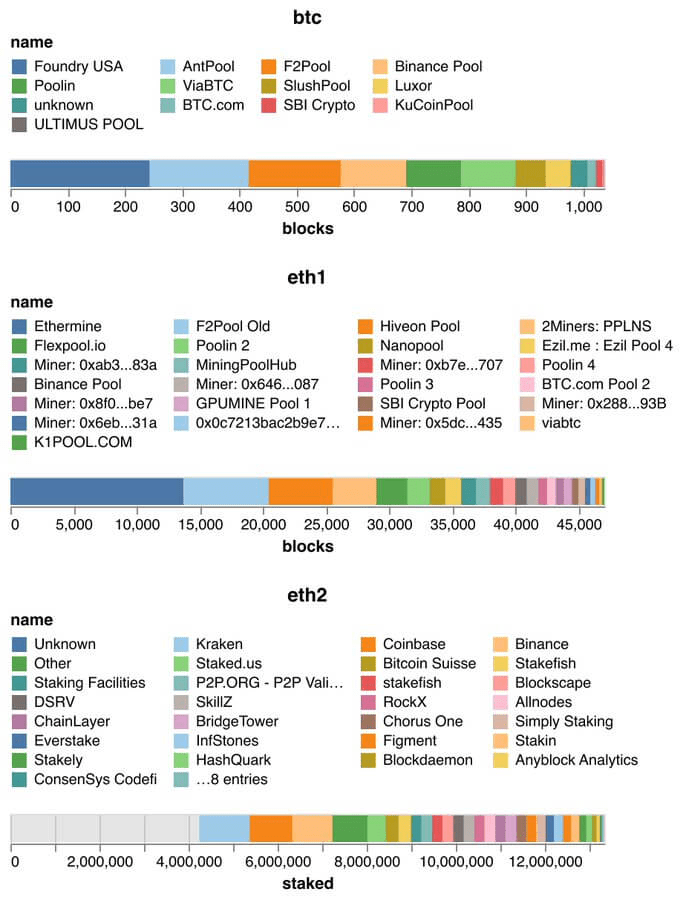
Source: @bantg
Potential challenges for Ethereum
1. Centralization
Many PoW advocates believe that PoS could lead the chain to be more centralized. This is because some people, particularly retail users, could delegate their stake to the biggest providers.
We’ve seen this happen before in the liquid staking derivative space with Lido, who dominate the market. Lido currently manage more than 30% of all staked Ethereum. Coinbase, Kraken and Binance make up almost another 30%.
However, Lido uses more than 30 different entities to run actual validator nodes on the beacon chain. Furthermore, alternatives like the decentralized Rocket Pool staking protocol have gathered significant traction; Rocket Pool now runs more than 1,400 validators on the chain.
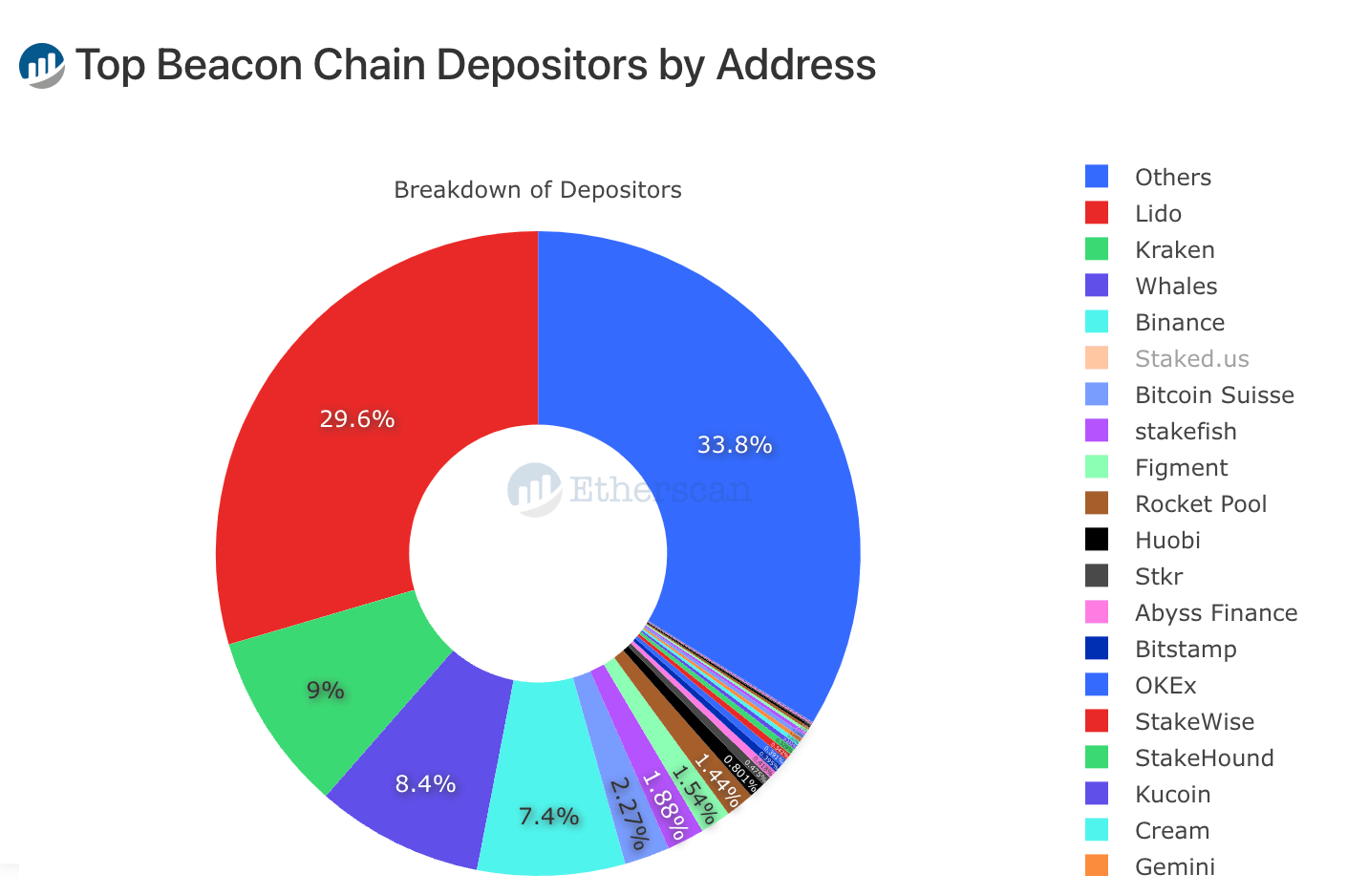
Source: Etherscan
2. Censorship risk
Potential centralization inevitably brings censorship risks. In this case, it would mean the biggest staking providers colluding to censor certain transactions or entities.
While possible in theory, if there are independent validators that are not censoring, transactions will still get included and entities that are trying to censor will be punished through the slashing mechanism.
3. Unavailable withdrawals
Withdrawals won’t be possible for months after The Merge and this brings risk.
The slashing mechanism in ETH 2.0, which punishes validators for dangerous or unwanted behavior and/or inactivity, might penalize some of the staking providers if they don’t fulfil their duties.
If the validators have taken in retail funds to finance their staking operation without the ability to withdraw, they could pass losses on to unsuspecting consumers.
Myths surrounding The Merge
With speculation spreading and numerous misconceptions online, researchers at the Ethereum foundation published an article debunking the myths surrounding The Merge.
Possibly the biggest misunderstanding is that PoS will simply replace PoW as part of the Ethereum node consensus mechanism, including its governance. The Ethereum governance will remain off-chain as it has always been, and validators will not be able to directly influence the development of the protocol with their stakes.
Upgrades and improvements will remain open and transparent through the EIP (Ethereum improvement proposal) process that is accessible for everyone.
Dive into crypto with Skrill
- Buy and sell over 40 different cryptocurrencies, including Ethereum
- Automate your trades with a range of simple features
- Earn points and be rewarded with Skrill's loyalty programme, Knect
Cryptocurrencies are unregulated in the UK. Capital Gains Tax or other taxes may apply. The value of investments is variable and can go down as well as up.


